Cell Cycle and Cell Division (कोशिका चक्र और कोशिका विभाजन)
Cell division एक fundamental process है जो सभी living organisms में growth, repair और reproduction के लिए आवश्यक है।
Cell division के द्वारा नई cells बनती हैं, जो parent cell से identical या genetic variation के साथ हो सकती हैं।
इस chapter में हम सीखेंगे कि कैसे cells अपने life cycle को complete करते हैं, और अलग-अलग प्रकार के cell division जैसे mitosis और meiosis क्यों और कैसे होते हैं।
Key Points (मुख्य बिंदु)
- Cell cycle – एक sequence of events है जिससे cell grow, replicate और divide करता है।
- Cell cycle में मुख्य चरण – Interphase और M-phase होते हैं।
- Mitosis – somatic cells के लिए responsible, genetically identical daughter cells बनाता है।
- Meiosis – reproductive cells (gametes) के लिए, genetic variation सुनिश्चित करता है।
- Cell cycle regulation और checkpoints – ensure करते हैं कि division सही तरीके से हो।
Cell division और cell cycle सभी multicellular organisms में growth और survival के लिए आवश्यक हैं।
Errors in cell cycle regulation lead to disorders like cancer.
Cell Cycle (कोशिका चक्र)
Cell cycle एक orderly sequence of events है, जिसके द्वारा cell grow करता है, DNA replicate होता है और अंत में division द्वारा दो daughter cells बनती हैं।
Cell cycle सुनिश्चित करता है कि नई cells accurately और efficiently बनाई जाएं।
1. Phases of Cell Cycle (कोशिका चक्र के चरण)
| Phase (चरण) | Description (विवरण) | Key Events (मुख्य घटनाएँ) |
| G1 Phase (Gap 1) | Cell growth and preparation for DNA replication | Protein synthesis, organelle duplication, cell size increases |
| S Phase (Synthesis) | DNA replication occurs | Each chromosome duplicates to form sister chromatids |
| G2 Phase (Gap 2) | Preparation for mitosis | Protein synthesis, spindle formation, DNA repair if needed |
| M Phase (Mitosis / Meiosis) | Cell division occurs | Division of nucleus (karyokinesis) and cytoplasm (cytokinesis) |
| G0 Phase (Resting) | Non-dividing, quiescent phase | Cells perform normal functions; e.g., neurons, muscle cells |
2. Important Points (महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु)
- Interphase = G1 + S + G2; cell actively grows और prepares for division।
- Checkpoints: G1 checkpoint, G2 checkpoint, M checkpoint – ensure errors are corrected before progression.
- Cell cycle regulation ensures proper growth, DNA integrity और prevents uncontrolled division (cancer prevention).
Cell cycle की सही regulation जीवन के लिए अत्यंत आवश्यक है।
Uncontrolled cell division → tumors और cancer का कारण बन सकता है।
Cell cycle का अध्ययन cancer research और regenerative medicine में महत्वपूर्ण है।
Phases of Cell Cycle (कोशिका चक्र के चरण)
Cell cycle मुख्य रूप से पाँच phases में विभाजित होता है: G1, S, G2, M, और G0.
इनमें से G1, S और G2 को मिलाकर Interphase कहते हैं। M phase में actual cell division होता है।
1. G1 Phase (Gap 1 / Growth 1)
- Cell size बढ़ता है और metabolic activities active होती हैं।
- Protein synthesis और organelle duplication होता है।
- G1 checkpoint: cell DNA replication के लिए ready है या नहीं यह जांचता है।
2. S Phase (Synthesis)
- DNA replication होती है।
- हर chromosome दो sister chromatids में duplicate होता है।
- Histone proteins का synthesis भी होता है।
3. G2 Phase (Gap 2 / Growth 2)
- Cell division के लिए preparation होती है।
- Spindle fibers बनते हैं और DNA repair mechanisms active रहते हैं।
- G2 checkpoint ensures कि कोई error DNA replication में न हो।
4. M Phase (Mitosis / Meiosis) – Cell Division
M phase में cell का nucleus और cytoplasm divide होते हैं।
M phase दो मुख्य प्रकार का होता है:
Mitosis (सामान्य कोशिका विभाजन)
- Somatic cells में होता है।
- Genetically identical daughter cells बनते हैं।
- Stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase + Cytokinesis।
Meiosis (संयुग्मन विभाजन / Gamete Formation)
- Reproductive cells (gametes) में होता है।
- Genetic variation सुनिश्चित करता है।
- Two successive divisions: Meiosis I and Meiosis II।
- Chromosome number daughter cells में आधा (haploid) होता है।
5. G0 Phase (Resting Phase)
- Non-dividing, quiescent cells perform normal functions।
- Example: Neurons, muscle cells.
M phase ensures proper distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
Errors during M phase can lead to mutations, cancer, or cell death.
Mitosis Stages (कोशिका विभाजन के चरण)
Mitosis एक orderly process है जिसमें nucleus divide होता है और genetically identical daughter nuclei बनते हैं।
Mitosis को चार main stages में विभाजित किया जाता है: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
1. Prophase (प्रोफेज)
- Chromatin fibers condense होकर chromosomes बन जाते हैं।
- Each chromosome दो sister chromatids से मिलकर बनता है, centromere से जुड़े रहते हैं।
- Nuclear membrane और nucleolus धीरे-धीरे disappear होते हैं।
- Spindle fibers form होना शुरू होते हैं (centrosomes से)।
2. Metaphase (मेटाफेज)
- Chromosomes spindle fibers के माध्यम से cell के equatorial plane (metaphase plate) पर line up होते हैं।
- Centromere spindle fibers से जुड़ा रहता है।
- Chromosome alignment ensures कि हर daughter cell को correct number of chromosomes मिले।
3. Anaphase (एनोफेज)
- Sister chromatids centromere से अलग होकर opposite poles की ओर खिंचते हैं।
- Chromatids अब individual chromosomes कहलाते हैं।
- Spindle fibers contract होते हैं, ensuring proper chromosome segregation।
4. Telophase (टेलोफेज)
- Chromosomes poles पर पहुँच जाते हैं और gradually decondense होकर chromatin बन जाते हैं।
- Nuclear membrane और nucleolus reform होते हैं।
- Spindle fibers disappear हो जाते हैं।
- Cytokinesis अक्सर Telophase के साथ शुरू होती है, जिससे two daughter cells बनते हैं।
Mitosis के ये चार stages ensure करते हैं कि हर daughter cell को identical genetic material मिले।
Errors in any stage → aneuploidy या genetic disorders का कारण बन सकते हैं।
Mitosis vs Meiosis – Stages Comparison (सारणी)
| Stage (चरण) | Mitosis (सामान्य विभाजन) | Meiosis I (पहला विभाजन) | Meiosis II (दूसरा विभाजन) |
| Prophase | Chromosomes condense, spindle forms, nuclear membrane disappears | Homologous chromosomes pair (synapsis), crossing over occurs, spindle forms | Chromosomes condense, spindle forms, nuclear membrane disappears |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes align at metaphase plate | Homologous pairs align at metaphase plate | Chromosomes align individually at metaphase plate |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate to opposite poles | Homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles | Sister chromatids separate to opposite poles |
| Telophase | Nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes decondense, cytokinesis occurs | Nuclear membrane may reform, cytokinesis occurs → two haploid cells | Nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes decondense, cytokinesis occurs → four haploid cells |
| Outcome | Two genetically identical diploid cells | Two genetically varied haploid cells | Four genetically varied haploid cells |
Cytokinesis (साइटोकाइनेसिस)
Cytokinesis वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें cell का cytoplasm divide होकर दो अलग-अलग daughter cells बनता है।
यह cell division का अंतिम चरण है और Mitosis या Meiosis के बाद होता है।
Cytokinesis ensures कि हर daughter cell के पास proper cytoplasm, organelles और nutrients हों।
Types of Cytokinesis (साइटोकाइनेसिस के प्रकार)
| Type (प्रकार) | Occurs In (कहाँ होता है) | Mechanism (तंत्र) |
| Animal Cells | Animal cells (somatic) | Cleavage furrow forms at the equator → actin-myosin contractile ring pinches the cell into two |
| Plant Cells | Plant cells | Cell plate forms at the center → grows outward and fuses with cell wall → two daughter cells |
Key Points (मुख्य बिंदु)
- Cytokinesis is different in plant and animal cells due to rigid cell wall in plants.
- Ensures equal distribution of cytoplasm and organelles between daughter cells.
- Occurs immediately after telophase of mitosis or meiosis.
Cytokinesis completes the cell division process. Without cytokinesis, cell would have two nuclei (binucleated cell).
Significance of Mitosis (माइटोसिस का महत्व)
Mitosis एक fundamental process है जो सभी multicellular organisms में growth, repair और reproduction के लिए आवश्यक है।
यह ensure करता है कि daughter cells genetically identical हों और हर cell में proper genetic material हो।
1. Growth (विकास)
- Mitosis द्वारा नए cells बनते हैं जो organism के growth में योगदान देते हैं।
- Example: Plants और animals में tissues बढ़ने के लिए cells divide होते हैं।
2. Repair and Regeneration (मरम्मत और पुनर्जनन)
- Injured tissues में damaged cells को replace करने के लिए mitosis होता है।
- Example: Skin और liver tissue regeneration।
3. Asexual Reproduction (अलैंगिक प्रजनन)
- Some organisms में, जैसे amoeba, hydra, mitosis के द्वारा reproduction होती है।
- Daughter cells parent cells के identical होते हैं।
4. Genetic Stability (आनुवंशिक स्थिरता)
- Mitosis सुनिश्चित करता है कि daughter cells में identical genetic information हो।
- Chromosome number constant रहता है, जिससे organism की species stability बनी रहती है।
5. Tissue Maintenance (ऊतक संरक्षण)
- Body के tissues में continuously cell replacement की आवश्यकता होती है।
- Mitosis old and worn-out cells को replace करता है।
Mitosis की सही functioning जीवन के लिए आवश्यक है।
Errors in mitosis → cancer, mutations, or abnormal cell growth हो सकते हैं।
Meiosis (संयुग्मन विभाजन)
Meiosis वह special type का cell division है जो reproductive cells (gametes) में होता है।
इस process में chromosome number आधा हो जाता है (diploid → haploid) और genetic variation पैदा होती है।
Meiosis sexual reproduction के लिए essential है।
1. Phases of Meiosis (मायोसिस के चरण)
| Phase (चरण) | Meiosis I (पहला विभाजन) | Meiosis II (दूसरा विभाजन) |
| Prophase | Homologous chromosomes pair (synapsis) and crossing over occurs; spindle forms; nuclear membrane disappears | Chromosomes condense, spindle forms, nuclear membrane disappears |
| Metaphase | Homologous pairs align at metaphase plate | Chromosomes align individually at metaphase plate |
| Anaphase | Homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles | Sister chromatids separate to opposite poles |
| Telophase | Chromosomes may decondense, nuclear membrane may reform; cytokinesis occurs → two haploid cells | Chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane reforms, cytokinesis occurs → four haploid cells |
| Outcome | Two genetically varied haploid cells | Four genetically varied haploid cells |
2. Key Features of Meiosis (मुख्य विशेषताएँ)
- Reduces chromosome number by half (diploid → haploid)
- Crossing over during Prophase I creates genetic variation
- Ensures gametes have unique combination of genes
- Essential for sexual reproduction and evolution
Meiosis creates genetic diversity which is important for adaptation and evolution.
Errors during meiosis → aneuploidy, Down syndrome, or other chromosomal disorders.
Meiosis I – Prophase I (पहला विभाजन – प्रोफेज I)
Meiosis I वह stage है जिसमें homologous chromosomes separate होते हैं।
इसमें Prophase I सबसे लंबा और सबसे महत्वपूर्ण phase है क्योंकि genetic variation इसी दौरान generate होती है।
Substages of Prophase I (Prophase I के उपचरण)
| Substage (उपचरण) | Events (मुख्य घटनाएँ) |
| Leptotene | Chromosomes start condensing; each is a single thread; homologous chromosomes begin finding each other |
| Zygotene | Homologous chromosomes pair (synapsis) forming bivalents; synaptonemal complex forms |
| Pachytene | Chromosomes thicken; crossing over occurs at chiasmata → genetic recombination |
| Diplotene | Synaptonemal complex dissolves; homologous chromosomes start separating but remain connected at chiasmata |
| Diakinesis | Chromosomes fully condensed; nucleolus disappears; nuclear membrane breaks down; spindle fibers form |
Key Features of Prophase I (मुख्य विशेषताएँ)
- Longest phase of Meiosis
- Crossing over generates genetic variation
- Formation of bivalents ensures proper segregation of homologous chromosomes
- Prepares cell for Metaphase I alignment
Prophase I के दौरान होने वाला crossing over evolution और genetic diversity के लिए crucial है।
Errors in this phase → genetic disorders या infertility का कारण बन सकते हैं।
Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I
Meiosis I में Prophase I के बाद chromosomes homologous pairs में align होते हैं और फिर अलग होते हैं।
यहाँ Metaphase I, Anaphase I और Telophase I के मुख्य घटनाओं का विवरण है।
1. Metaphase I (मेटाफेज I)
- Homologous chromosomes (bivalents) spindle fibers की मदद से cell के equatorial plate पर align होते हैं।
- Orientation random होती है (independent assortment) → genetic variation बढ़ती है।
- Each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids, जो centromere से जुड़े होते हैं।
2. Anaphase I (एनोफेज I)
- Homologous chromosomes अलग होकर opposite poles की ओर move करते हैं।
- Sister chromatids अब भी centromere से जुड़े रहते हैं।
- Reduction division होती है, यानी chromosome number आधा हो जाता है (diploid → haploid)।
3. Telophase I (टेलोफेज I)
- Chromosomes poles पर पहुँच जाते हैं और कुछ cells में nuclear membrane reform होती है।
- Chromosomes partially decondense हो सकते हैं।
- Cytokinesis होता है → दो haploid daughter cells बनते हैं, प्रत्येक में half chromosome number।
Meiosis I में reduction division और genetic variation ensure होती है।
Errors in this stage → nondisjunction → Down syndrome, Turner syndrome आदि हो सकते हैं।
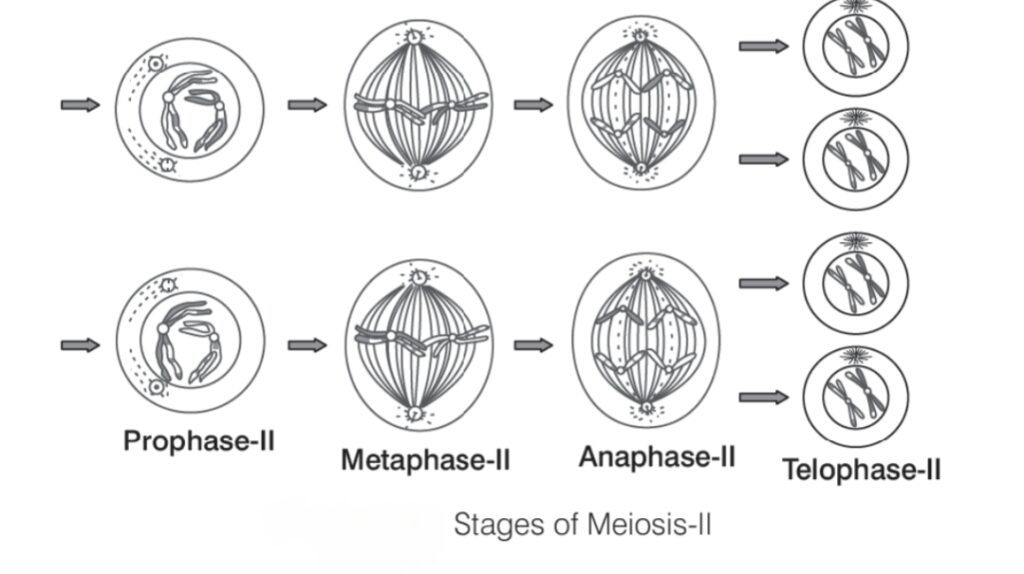
Meiosis II (दूसरा विभाजन)
Meiosis II essentially resembles Mitosis but occurs in haploid cells formed after Meiosis I.
इसमें sister chromatids अलग होकर चार genetically varied haploid gametes बनाते हैं।
1. Prophase II (प्रोफेज II)
- Chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form.
- Nuclear membrane disappears if it reformed during Telophase I.
- Each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids.
2. Metaphase II (मेटाफेज II)
- Chromosomes align individually along the equatorial plate.
- Spindle fibers attach to centromeres of sister chromatids.
3. Anaphase II (एनोफेज II)
- Sister chromatids separate at centromere and move to opposite poles.
- Each chromatid is now considered an individual chromosome.
4. Telophase II (टेलोफेज II)
- Chromosomes reach the poles and begin to decondense.
- Nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes.
- Cytokinesis occurs → total of four haploid daughter cells produced.
Key Features of Meiosis II (मुख्य विशेषताएँ)
- Occurs in haploid cells from Meiosis I.
- Similar to mitosis but produces genetically varied gametes.
- Ensures sister chromatids separate and maintain haploid number.
- Important for sexual reproduction in animals and plants.
Meiosis II ensures each gamete receives one copy of each chromosome.
Errors in this stage can lead to aneuploidy or genetic disorders in offspring.
Significance of Meiosis (मायोसिस का महत्व)
Meiosis sexual reproduction के लिए essential है। यह diploid cells को haploid gametes में बदल देता है और genetic variation पैदा करता है।
यह process organisms में evolution और species diversity के लिए crucial है।
1. Reduction of Chromosome Number (क्रोमोसोम संख्या का घटाव)
- Meiosis में chromosome number आधा हो जाता है (2n → n)।
- इससे fertilization के बाद chromosome number normal diploid रहता है।
2. Genetic Variation (आनुवंशिक विविधता)
- Crossing over during Prophase I और independent assortment के कारण genetic recombination होती है।
- Offspring में parent से अलग नए combinations उत्पन्न होते हैं।
3. Formation of Gametes (गैमीट्स का निर्माण)
- Meiosis से haploid sperm और egg cells बनते हैं।
- Ensures sexual reproduction के लिए correct chromosome number।
4. Evolution and Adaptation (संचय और अनुकूलन)
- Genetic variation allows species to adapt to changing environments।
- Important for natural selection और evolution के लिए।
Meiosis ensures genetic stability across generations while creating diversity.
Errors during meiosis → chromosomal disorders जैसे Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome हो सकते हैं।
Cell Division (Mitosis & Meiosis)
- Which phase of mitosis involves separation of sister chromatids?
(a) Prophase (b) Metaphase (c) Anaphase (d) Telophase
Answer: (c) Anaphase - During meiosis, crossing over occurs in:
(a) Metaphase I (b) Prophase I (c) Anaphase I (d) Telophase I
Answer: (b) Prophase I - How many daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis?
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 8 (d) 1
Answer: (b) 4 - Chromosome number remains same in daughter cells during:
(a) Mitosis (b) Meiosis I (c) Meiosis II (d) None
Answer: (a) Mitosis - Reduction division occurs in:
(a) Mitosis (b) Meiosis I (c) Meiosis II (d) Binary fission
Answer: (b) Meiosis I - Independent assortment of chromosomes occurs in:
(a) Metaphase I of meiosis (b) Anaphase I (c) Metaphase of mitosis (d) Telophase
Answer: (a) Metaphase I of meiosis - Sister chromatids separate in:
(a) Mitosis anaphase & Meiosis II anaphase (b) Meiosis I anaphase only
(c) Prophase I (d) Metaphase II
Answer: (a) Mitosis anaphase & Meiosis II anaphase - Homologous chromosomes pair to form bivalents during:
(a) Prophase I (b) Metaphase I (c) Anaphase I (d) Telophase I
Answer: (a) Prophase I - Cytokinesis occurs:
(a) Only after mitosis (b) Only after meiosis (c) After mitosis and meiosis (d) During interphase
Answer: (c) After mitosis and meiosis - Which phase of mitosis is characterized by chromosome alignment at the equatorial plate?
(a) Prophase (b) Metaphase (c) Anaphase (d) Telophase
Answer: (b) Metaphase - Which of the following is true about meiosis II?
(a) Chromosome number reduces (b) Sister chromatids separate (c) Homologous chromosomes separate (d) Crossing over occurs
Answer: (b) Sister chromatids separate - In which type of cell division, daughter cells are genetically identical?
(a) Mitosis (b) Meiosis (c) Both (d) None
Answer: (a) Mitosis - Binucleated cell is formed if which process fails?
(a) Prophase (b) Cytokinesis (c) Metaphase (d) Telophase
Answer: (b) Cytokinesis - Chiasmata are observed in:
(a) Prophase I (b) Metaphase II (c) Anaphase II (d) Telophase II
Answer: (a) Prophase I - Which phase of meiosis ensures genetic variation?
(a) Crossing over during Prophase I (b) Anaphase I segregation (c) Metaphase II alignment (d) Telophase II
Answer: (a) Crossing over during Prophase I - Which stage directly follows telophase of mitosis?
(a) Interphase (b) Prophase II (c) Cytokinesis (d) Anaphase
Answer: (a) Interphase - Reductional division refers to:
(a) Meiosis I (b) Meiosis II (c) Mitosis (d) Binary fission
Answer: (a) Meiosis I - During which phase do nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear?
(a) Prophase (b) Metaphase (c) Anaphase (d) Telophase
Answer: (a) Prophase - Gametes formed after meiosis are:
(a) Diploid (b) Haploid (c) Triploid (d) Polyploid
Answer: (b) Haploid - Which process maintains chromosome number across generations?
(a) Mitosis (b) Meiosis (c) Fertilization (d) All of these
Answer: (a) Mitosis
External Links – Cell Division (Mitosis & Meiosis)
- NCERT Official Website – Class 11 Biology Textbook
- Khan Academy – Cell Division (Mitosis & Meiosis)
- Biology Online – Meiosis
- Learn CBSE – Mitosis & Meiosis Notes
- Britannica – Mitosis Overview
Read more chapters